Food & Obesity
India also leads the world with over 212 million cases of diabetes while a third of Indians suffer from hypertension Many in this large pool of patients are likely to have a common condition: obesity.
As per the National Family Health Survey-5 (2019-21), 24% of Indian women and 23% of Indian men are overweight or obese, in other words roughly one in four adults is overweight or obese.
Obesity is linked to more than 200 serious health conditions.Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. It has also been called a chronic disease. The debate on whether obesity should be classified as a disease continues in the U.K. and many other countries worldwide.
People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's weight divided by the square of the person's height—is over 30 kg/m2; the range 25–30 kg/m2 is defined as overweight. Some East Asian countries use lower values to calculate obesity.
In India, a person is considered overweight if their Body Mass Index (BMI) is between 23.0 and 24.9 kg/m², and obese if their BMI is 25 kg/m² or higher. India has the third largest obese population in the world after USA and China, as per WHO estimates. Morbid obesity affects 5% of the country's population.
 |
| Source - Lancet |
A BMI of ≥ 35 kg/m2 and experiencing obesity-related health conditions or ≥ 40 or 45 kg/m2 is morbid obesity.
Abdominal or visceral obesity, also known as central obesity, is considered the more serious form of fat distribution, as it predisposes individuals to various metabolic disorders and diseases. Asian Indians are more susceptible to abdominal obesity and accumulation of visceral fat, making them more vulnerable to associated health risks.
Abdominal or central obesity is defined as having a waist circumference of more than 80 cm in women and more than 94 cm in men.
Complex factors, including genetics, environment, diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of supportive policies and social and cultural circumstances can affect weight loss.
In India, the time and expense required for maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise are significant considerations.

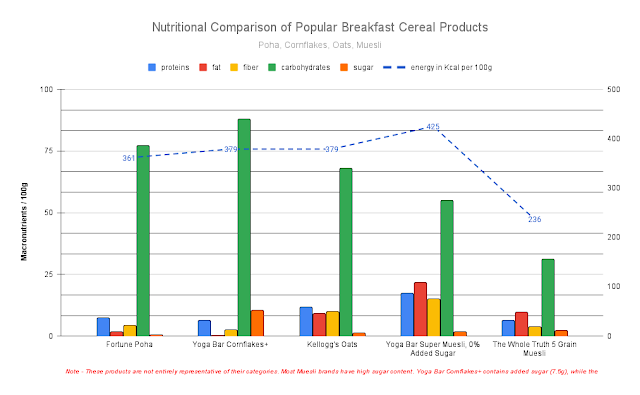


Comments
Post a Comment